Publications
-
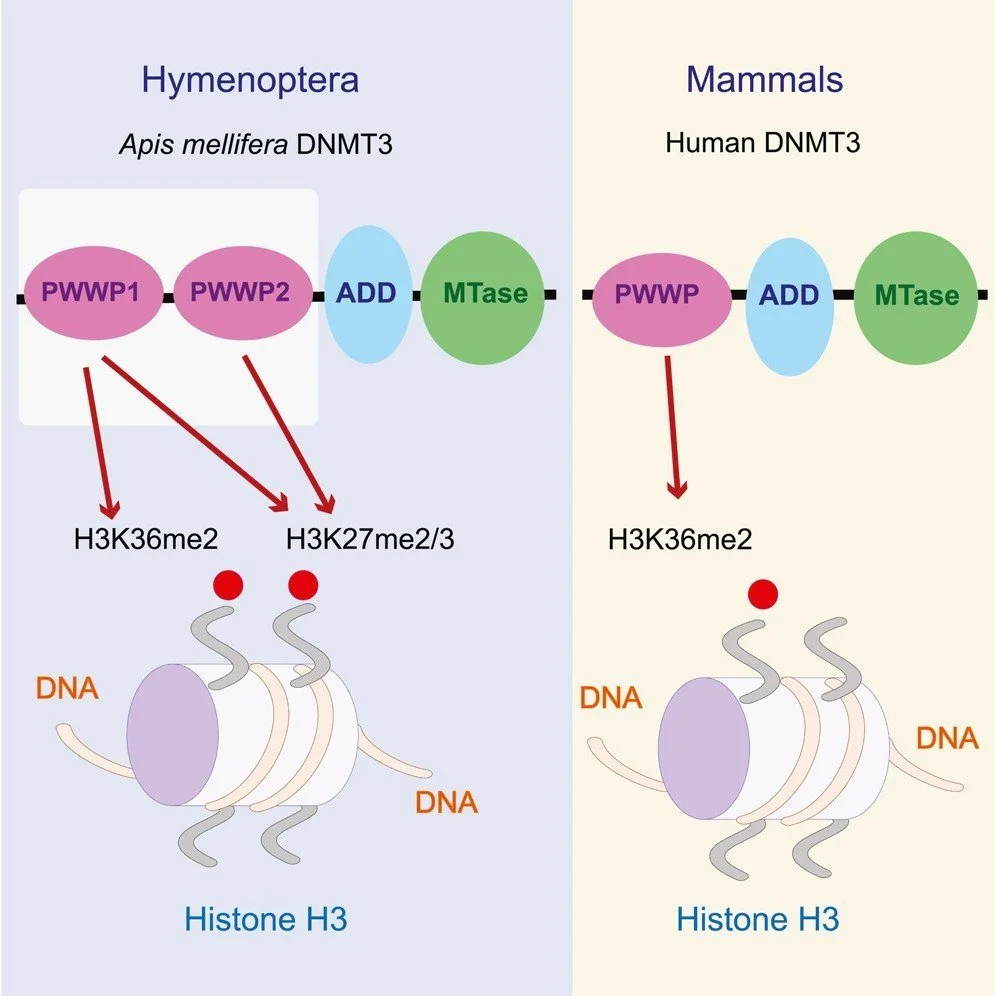
The PWWP domain and the evolution of unique DNA methylation toolkits in Hymenoptera
DNMT3 in Hymenoptera has a unique duplication of the essential PWWP domain. Using GST-tagged PWWP fusion proteins and histone arrays we show that these domains have gained new properties and represent the first case of PWWP domains binding to H3K27 chromatin modifications, including H3K27me3, a key modification that is important during development. Phylogenetic analyses of 107 genomes indicate that the duplicated PWWP domains separated into two sister clades, and their distinct binding capacities are supported by 3D modeling. Other features of this unique DNA methylation system include variable copies, losses, and duplications of DNMT1 and DNMT3, and combinatorial generations of DNMT3 isoforms including variants missing the catalytic domain. Some of these losses and duplications of are found only in parasitic wasps. We discuss our findings in the context of the crosstalk between DNA methylation and histone methylation, and the expanded potential of epigenomic modifications in Hymenoptera to drive evolutionary novelties.
-
Chromatin accessibility-based characterisation of brain gene regulatory networks in three distinct honey bee polyphenisms
The honey bee genome has the capacity to produce three phenotypically distinct organisms (two diploid female castes: queen and worker, and a haploid male drone). Previous studies have implicated metabolic flux acting via epigenetic regulation in directing nutrition-driven phenotypic plasticity in the honey bee. However, the cis-acting DNA regulatory elements that establish tissue and polyphenism -specific epigenomes and gene expression programmes, remain unclear. Using a high resolution multiomic approach including assay for transposase-accessible chromatin by sequencing (ATAC-seq), RNA-seq and ChIP-seq, we produce the first genome-wide maps of the regulatory landscape across all three adult honey bee phenotypes identifying > 5000 regulatory regions in queen, 7500 in worker and 6500 in drone, with the vast majority of these sites located within intronic regions. These regions are defined by positive enrichment of H3K27ac and depletion of H3K4me3 and show a positive correlation with gene expression. Using ATAC-seq footprinting we determine queen, worker and drone -specific transcription factor occupancy and uncover novel phenotype-specific regulatory networks identifying two key nuclear receptors that have previously been implicated in caste-determination and adult behavioural maturation in honey bees; ecdysone receptor and ultraspiracle. Collectively, this study provides novel insights into key gene regulatory networks that are associated with these distinct polyphenisms in the honey bee.
-

Phenotypically distinct female castes in honey bees are defined by alternative chromatin states during larval development
The capacity of the honey bee to produce three phenotypically distinct organisms (two female castes; queens and sterile workers, and haploid male drones) from one genotype represents one of the most remarkable examples of developmental plasticity in any phylum. The queen–worker morphological and reproductive divide is environmentally controlled during post-embryonic development by differential feeding. Previous studies implicated metabolic flux acting via epigenetic regulation, in particular DNA methylation and microRNAs, in establishing distinct patterns of gene expression underlying caste-specific developmental trajectories. We produce the first genome-wide maps of chromatin structure in the honey bee at a key larval stage in which developmental canalization into queen or worker is virtually irreversible. We find extensive genome-wide differences in H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K36me3, many of which correlate with caste-specific transcription. Furthermore, we identify H3K27ac as a key chromatin modification, with caste-specific regions of intronic H3K27ac directing the worker caste. These regions may harbor the first examples of caste-specific enhancer elements in the honey bee. Our results demonstrate a key role for chromatin modifications in the establishment and maintenance of caste-specific transcriptional programs in the honey bee. We show that at 96 h of larval growth, the queen-specific chromatin pattern is already established, whereas the worker determination is not, thus providing experimental support for the perceived timing of this critical point in developmental heterochrony in two types of honey bee females. In a broader context, our study provides novel data on environmentally regulated organismal plasticity and the molecular foundation of the evolutionary origins of eusociality.
All Publications
2025:
A dynamic histone-based chromatin regulatory toolkit underpins genome and developmental evolution in an invertebrate clade
Francisco M. Martín-Zamora, Joby Cole, Rory D. Donnellan, Kero Guynes, Allan M. Carrillo-Baltodano, Mark J. Dickman, Paul J. Hurd & José M. Martín-Durán
Genome Biology volume 26, Article number: 160 (2025)
2024:
Annelid methylomes reveal ancestral developmental and aging-associated epigenetic erosion across Bilateria
Kero Guynes, Luke A. Sarre, Allan M. Carrillo-Baltodano, Billie E. Davies, Lan Xu, Yan Liang, Francisco M. Martín-Zamora, Paul J. Hurd, Alex de Mendoza & José M. Martín-Durán
Genome Biology, Springer Nature vol. 25 (1), 204-204.
2023:
The PWWP domain and the evolution of unique DNA methylation toolkits in Hymenoptera
Robert Kucharski, Nancy Ellis, Tomasz P. Jurkowski, Paul J. Hurd, Ryszard Maleszka
Iscience, Cell Press vol. 26 (11)Systemic Mutational Rescue in Escherichia Coli Elicited by a Valency Dependent, High Affinity Protein DNA Interaction
Hurd, P.J. Al-Swailem, A.M. Bin Dukhyil, A.A.A. Sheikh, Q.I. Al-Ghanim, A.A. Alfageih, L. Matin, M. Yueh Ting, L.u. Abdalgelel, A. Florence, J. Mohammed Al- Shemirti, Al Harbi, S. Brown, P.E. Hornby, D.P.
Journal of Bioinformatics and Systems Biology. 6 (2023): 97-109
2022:
Chromatin accessibility-based characterisation of brain gene regulatory networks in three distinct honey bee polyphenisms
Robert Lowe , Marek Wojciechowski , Nancy Ellis , Paul J Hurd
Nucleic Acids Research, Oxford University Press
2021:
Novel structure in the nuclei of honey bee brain neurons revealed by immunostaining
Paul J. Hurd, Kornelia Grübel, Marek Wojciechowski, Ryszard Maleszka & Wolfgang Rössler
Scientific Reports, Nature Publishing Group vol. 11 (1)Dataset of the next-generation sequencing of variable 16S rRNA from bacteria and ITS2 regions from fungi and plants derived from honeybees kept under anthropogenic landscapes
Marek Gancarz, Paul J. Hurd, Przemyslaw Latoch, Andrew Polaszek, Joanna Michalska-Madej, Łukasz Grochowalski, Dominik Strapagiel, Sebastian Gnat, Daniel Załuski, Robert Rusinek, Agata L. Starosta, Patcharin Krutmuang, Raquel Martín Hernández, Mariano Higes Pascual & Aneta A. Ptaszyńska
Data in Brief, Elsevier vol. 36Amplicon Sequencing of Variable 16S rRNA from Bacteria and ITS2 Regions from Fungi and Plants, Reveals Honeybee Susceptibility to Diseases Results from Their Forage Availability under Anthropogenic Landscapes
Aneta A. Ptaszyńska, Przemyslaw Latoch, Paul J. Hurd, Andrew Polaszek, Joanna Michalska-Madej, Łukasz Grochowalski, Dominik Strapagiel, Sebastian Gnat, Daniel Załuski, Marek Gancarz, Robert Rusinek, Patcharin Krutmuang, Raquel Martín Hernández, Mariano Higes Pascual & Agata L. Starosta
Pathogens, Mdpi vol. 10 (3)
2020:
Phenotypic responses to temperature in the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila
Vanessa Weber de Melo, Robert Lowe, Paul J. Hurd & Owen L. Petchey
Ecology and Evolution, Wiley
2019:
Acute social isolation alters neurogenomic state in songbird forebrain
Julia M. George, Zachary W. Bell, Daniel Condliffe, Kirstin Dohrer, Teresa Abaurrea, Karen Spencer, Albertine Leitão, Manfred Gahr, Paul J. Hurd & David F. Clayton
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
2018:
Phenotypically distinct female castes in honey bees are defined by alternative chromatin states during larval development
Marek Wojciechowski, Robert Lowe, Joanna Maleszka, Danyal Conn, Ryszard Maleszka & Paul J. Hurd
Genome Research, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory PressChanges in the bioelement content of summer and winter western honeybees (Apis mellifera) induced by Nosema ceranae infection
Aneta A. Ptaszyńska, Marek Gancarz, Paul J. Hurd, Grzegorz Borsuk, Dariusz Wiącek, Agnieszka Nawrocka, Aneta Strachecka, Daniel Załuski & Jerzy Paleolog
Plos One, Public Library of Science (Plos) vol. 13 (7)
2015:
Binding loci of RelA-containing nuclear factor-kappaB dimers in promoter regions of PHM1-31 myometrial smooth muscle cells
Victoria J. Cookon, Sarah L. Waite, Paul R. Heath, Paul J. Hurd, Saurabh V. Gandhi, Neil R. Chapman
Mol Hum Reprod vol. 21 (11), 865-883Arginine methylation and citrullination of splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich (SFPQ/PSF) regulates its association with mRNA
Ambrosius P. Snijders, Guillaume M. Hautbergue, Alex Bloom, James C. Williamson, Thomas C. Minshull, Helen L. Phillips, Simeon R. Mihaylov, Douglas T. Gjerde, David P. Hornby, Stuart A. Wilson, Paul J. Hurd and Mark J. Dickman
Rna vol. 21 (3), 347-359
2014:
S6 kinase 2 is bound to chromatin-nuclear matrix cellular fractions and is able to phosphorylate histone H3 at threonine 45 in vitro and in vivo
Heba M.S. Ismail, Paul J. Hurd, Mahmoud I.M. Khalil, Tony Kouzarides, Andrew Bannister, Ivan Gout
J Cell Biochem vol. 115 (6), 1048-1062
2013:
Epigenetic mechanisms in development and disease
Adele Murrell, Paul J. Hurd, Ian C. Wood
Biochem Soc Trans vol. 41 (3), 697-699Inactive or moderately active human promoters are enriched for inter-individual epialleles
Carolina Gemma, Sreeram V Ramagopalan, Thomas A Down, Huriya Beyan, Mohammed I Hawa, Michelle L Holland, Paul J Hurd, Gavin Giovannoni, R David Leslie, George C Ebers & Vardhman K Rakyan
Genome Biol vol. 14 (5)Extensive histone post-translational modification in honey bees
Mark J. Dickman, Robert Kucharski, Ryszard Maleszka, Paul J. Hurd
Insect Biochem Mol Biol vol. 43 (2), 125-137
2012:
Meeting preview
Adele Murrell, Paul J. Hurd, Ian C. Wood
The Biochemist, Portland Press vol. 34 (5)
2010:
The era of epigenetics
Paul J. Hurd
Brief Funct Genomics vol. 9 (5-6), 425-428Systems Biology for Ecology: From Molecules to Ecosystems
Kevin J. Purdy, Paul J. Hurd, Jordi Moya-Laraño, Mark Trimmer, Brian B. Oakley, Guy Woodward
Adv Ecol Res vol. 43, 87-149
2009:
Phosphorylation of histone H3 Thr-45 is linked to apoptosis
Paul J. Hurd, Andrew J. Bannister, Karen Halls, Mark A. Dawson, Michiel Vermeulen, Jesper V. Olsen, Heba Ismail, Joanna Somers, Matthias Mann, Tom Owen-Hughes, Ivan Gout, Tony Kouzarides
J Biol Chem vol. 284 (24), 16575-16583Advantages of next-generation sequencing versus the microarray in epigenetic research
Paul J. Hurd, Christopher J. Nelson
Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic vol. 8 (3), 174-183
2008:
Heritable gene repression through the action of a directed DNA methyltransferase at a chromosomal locus
Alexander E. Smith, Paul J. Hurd, Andrew J. Bannister, Tony Kouzarides, Kevin G. Ford
J Biol Chem vol. 283 (15), 9878-9885DNMT1 interacts with the developmental transcriptional repressor HESX1
Ezat Sajedi, Carles Gaston-Massuet, Cynthia L. Andoniadou, Massimo Signore, Paul J. Hurd, Mehul Dattani, Juan Pedro Martinez-Barbera
Biochim Biophys Acta vol. 1783 (1), 131-143
2007:
Directed de novo DNA methylation of a genomic locus leads to heritable transcriptional repression
Kevin G. Ford, Paul J. Hurd, Andrew J. Bannister, Tony Kouzarides, Alexander E. Smith
BLOOD. vol. 110 (11), 108A-108A
2006:
Dynamic distribution of the replacement histone variant H3.3 in the mouse oocyte and preimplantation embryos
Maria-Elena Torres-Padilla, Andrew J. Bannister, Paul J. Hurd, Tony Kouzarides and Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz
Int J Dev Biol vol. 50 (5), 455-461
2003:
The DNA methyltransferases associate with HP1 and the SUV39H1 histone methyltransferase
François Fuks, Paul J. Hurd, Rachel Deplus, Tony Kouzarides
Nucleic Acids Res vol. 31 (9), 2305-2312The Methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 links DNA methylation to histone methylation
François Fuks, Paul J. Hurd, Daniel Wolf, Xinsheng Nan, Adrian P. Bird, Tony Kouzarides
J Biol Chem vol. 278 (6), 4035-4040
2002:
Characterisation of site-biased DNA methyltransferases: specificity, affinity and subsite relationships
Andrew R. McNamara, Paul J. Hurd, Alexander E. F. Smith, Kevin G. Ford
Nucleic Acids Res vol. 30 (17), 3818-3830Zebularine: a novel DNA methylation inhibitor that forms a covalent complex with DNA methyltransferases
L. Zhou, X. Cheng, B.A. Connolly, M.J. Dickman, P.J. Hurd, D.P. Hornby
J Mol Biol vol. 321 (4), 591-599
1999:
Mechanism-based inhibition of C5-cytosine DNA methyltransferases by 2-H pyrimidinone
Paul J Hurd, Alan J Whitmarsh, Geoffrey S Baldwin, Sharon M Kelly, Jonathan P Waltho, Nicholas C Price, Bernard A Connolly, David P Hornby
Journal of Molecular Biology vol. 286 (2), 389-401
1995:
Expression Systems and Fusion Proteins
Hurd, P. J. and Hornby, D. P.
Proteins Labfax (N. C. Price ed.) BIOS Scientific Publishers/Academic Press, Oxford, UK. p.109 - 117